RSA Tutorial
Compare DSMs
- For CoSMoMVPA's copyright information and license terms, #
- see the COPYING file distributed with CoSMoMVPA. #
subjects = {'s01', 's02', 's03', 's04', 's05', 's06', 's07', 's08'};
masks = {'ev_mask.nii', 'vt_mask.nii'};
config = cosmo_config();
study_path = fullfile(config.tutorial_data_path, 'ak6');
In a nested loop over masks then subjects: load each dataset demean it, get DSM, save it in dsms
n_subjects = numel(subjects); n_masks = numel(masks); counter = 0; for m = 1:n_masks msk = masks{m}; for s = 1:length(subjects) sub = subjects{s}; sub_path = fullfile(study_path, sub); % load dataset ds_fn = fullfile(sub_path, 'glm_T_stats_perrun.nii'); mask_fn = fullfile(sub_path, msk); ds_full = cosmo_fmri_dataset(ds_fn, ... 'mask', mask_fn, ... 'targets', repmat(1:6, 1, 10)'); % compute average for each unique target ds = cosmo_fx(ds_full, @(x)mean(x, 1), 'targets', 1); % remove constant features ds = cosmo_remove_useless_data(ds); % demean % Comment this out to see the effects of demeaning vs. not ds.samples = bsxfun(@minus, ds.samples, mean(ds.samples, 1)); % compute the one-minus-correlation value for each pair of % targets. % (Hint: use cosmo_pdist with the 'correlation' argument) % >@@> dsm = cosmo_pdist(ds.samples, 'correlation'); % <@@< if counter == 0 % first dsm, allocate space n_pairs = numel(dsm); neural_dsms = zeros(n_subjects * n_masks, n_pairs); end % increase counter and store the dsm as the counter-th row in % 'neural_dsms' % >@@> counter = counter + 1; neural_dsms(counter, :) = dsm; % <@@< end end
Then add the v1 model and behavioral DSMs
models_path = fullfile(study_path, 'models'); load(fullfile(models_path, 'v1_model.mat')); load(fullfile(models_path, 'behav_sim.mat')); % add to dsms (hint: use comso_squareform) % >@@> v1_model_sf = cosmo_squareform(v1_model); behav_model_sf = cosmo_squareform(behav); % ensure row vector because Matlab and Octave return % row and column vectors, respectively dsms = [neural_dsms; v1_model_sf(:)'; behav_model_sf(:)']; % <@@<
Now visualize the cross-correlation matrix. Remember that 'cosmo_corr' (or the builtin 'corr') calculates correlation coefficients between columns and we want between rows, so the data has to be transposed.
% >@@> cc = cosmo_corr(dsms'); figure(); imagesc(cc); % <@@<
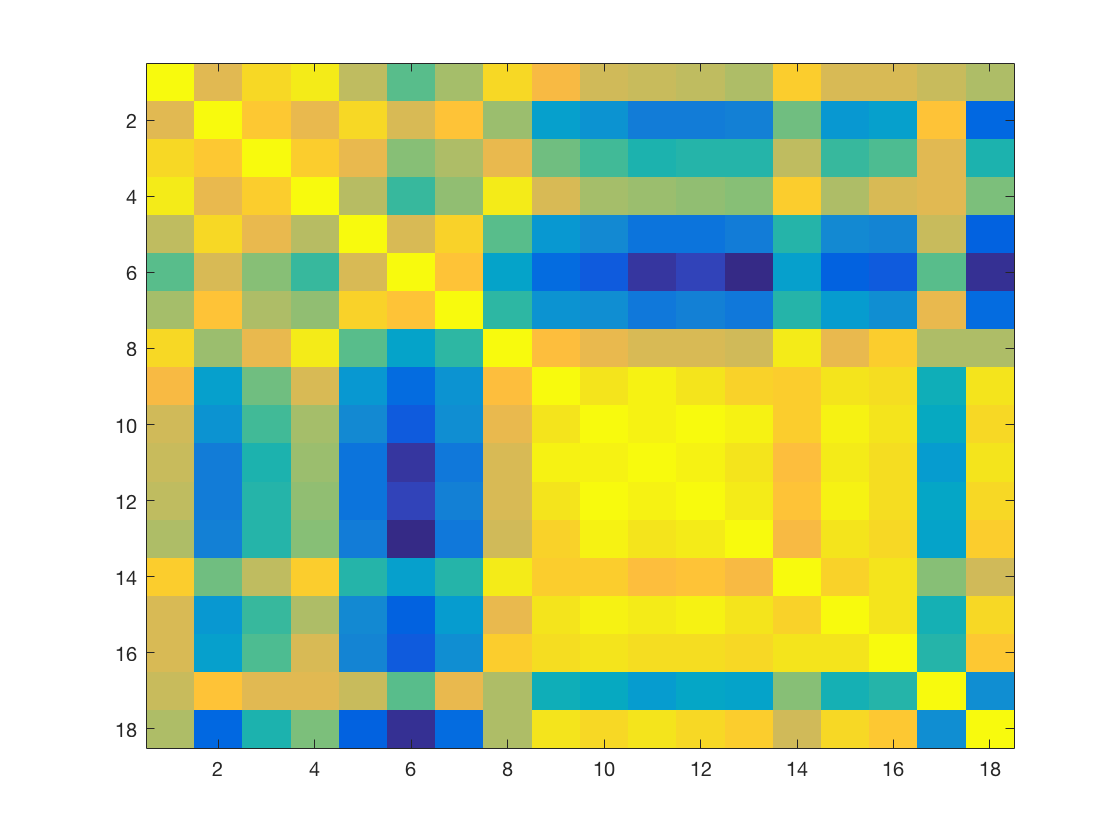
Now use the values in the last two rows of the cross correlation matrix to visualize the distributions in correlations between the neural similarities and the v1 model/behavioral ratings. Store the result in a matrix 'cc_models', which should have 8 rows (corresponding to the participants) and 4 columns (corresponding to EV and VT correlated with both models)
Rows 1 to 8: EV neural similarities Rows 9 to 16: VT neural similarities Row 17: EV model Row 18: behavioural similarities
% >@@> cc_models = [cc(1:8, 17) cc(9:16, 17) cc(1:8, 18) cc(9:16, 18)]; % <@@< labels = {'v1 model~EV', 'v1 model~VT', 'behav~EV', 'behav~VT'}; figure(); boxplot(cc_models); set(gca, 'XTick', [1:4], 'XTickLabel', labels);
