Example of de-meaning
- For CoSMoMVPA's copyright information and license terms, #
- see the COPYING file distributed with CoSMoMVPA. #
Contents
Generate random dataset
ds = cosmo_synthetic_dataset('nchunks', 4, 'ntargets', 3); % add some constant to all data ds.samples = ds.samples + 2; % show dataset subplot(2, 2, 1); imagesc(ds.samples, [-4 4]); title('before demeaning'); subplot(2, 2, 2); hist(ds.samples(:), 10); xlim([-6 6]);
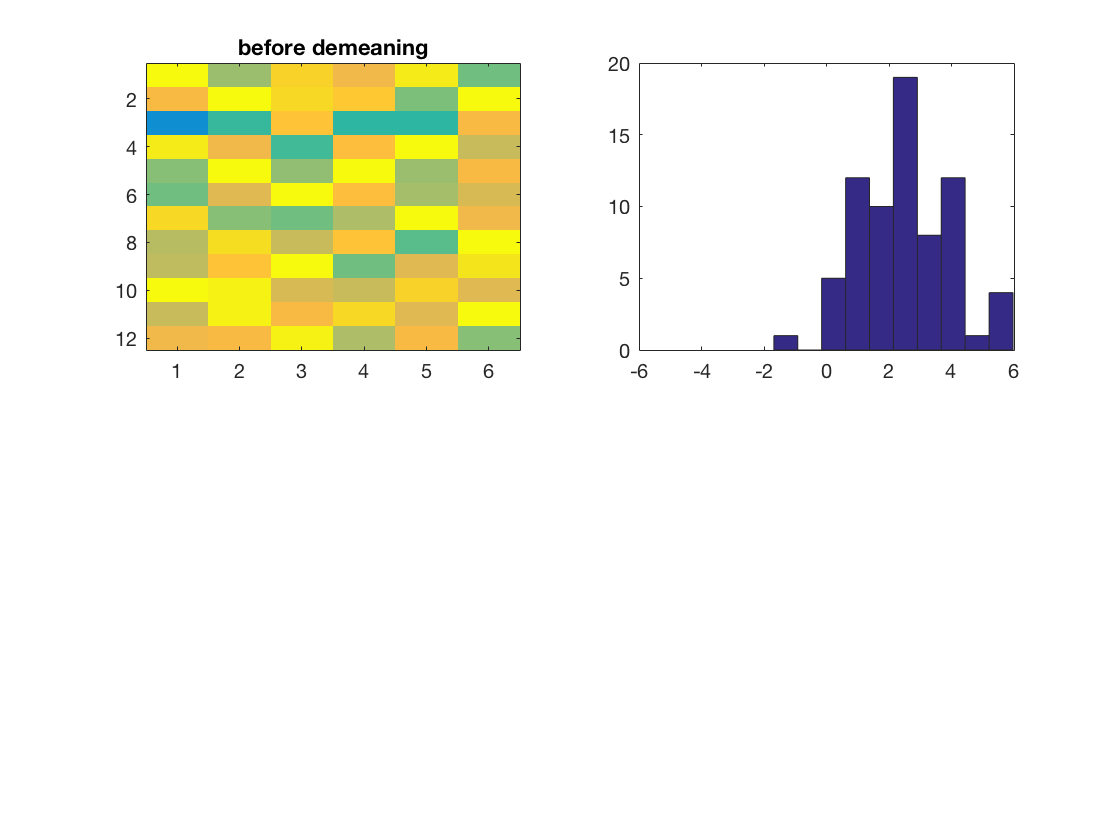
Split the dataset by chunks
>@@>
splits = cosmo_split(ds, {'chunks'}, 1);
% <@@<
nsplits = numel(splits);
% allocate space for output
outputs = cell(nsplits, 1);
% treat each element in splits separately, and subtract the mean for each
% feature separately
for k = 1:nsplits
d = splits{k};
% >@@>
% mean over samples, for each feature
mu = mean(d.samples, 1);
% subtract the mean.
% equivalent, but less efficient, is:
% nsamples=size(d.samples,1);
% d.samples=d.samples-repmat(mu,nsamples,1);
%
d.samples = bsxfun(@minus, d.samples, mu);
% <@@<
% store output
outputs{k} = d;
end
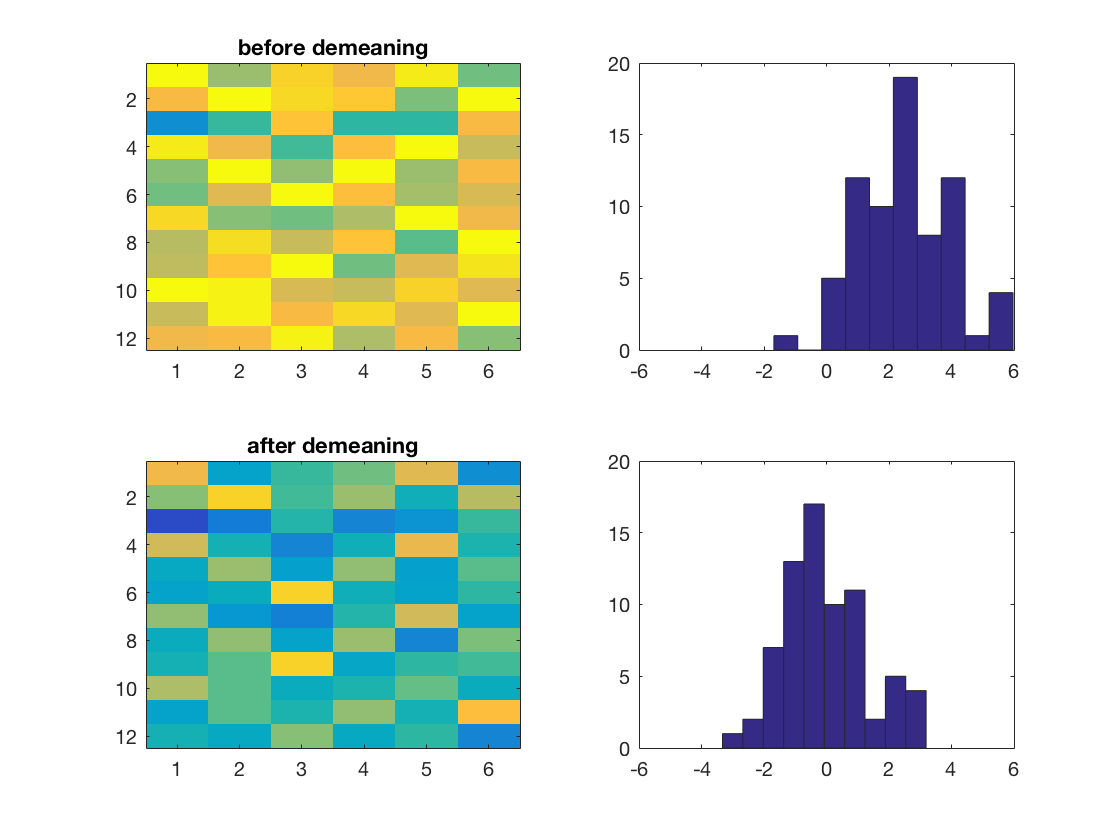
ds_demeaned = cosmo_stack(outputs);
% show dataset
subplot(2, 2, 3);
imagesc(ds_demeaned.samples, [-4 4]);
title('after demeaning');
subplot(2, 2, 4);
hist(ds_demeaned.samples(:), 10);
xlim([-6 6]);
Alternative approach to demeaning
% note: the samples in the output are in a different order than the input, % but otherwise the same demeaner = @(x)bsxfun(@minus, x, mean(x, 1)); % function handle as helper ds_demeaned_alt = cosmo_fx(ds, demeaner, 'chunks');